Table of Contents
Introduction
Data has become the lifeblood of modern businesses. But not all data needs to be processed the same way—or at the same speed. For decision-makers, the question often comes down to one key comparison: Real-Time vs. Batch Data Processing.
Choosing between these two methods can significantly impact your operations, customer experience, and long-term efficiency. Do you need instant insights for fraud detection and personalized marketing? Or do you need to crunch massive datasets overnight for payroll or regulatory reporting?
In this article, we’ll break down the differences between real-time data processing and batch data processing, explore common data processing strategies, and help you determine which approach best fits your business needs.
? Looking to implement a tailored solution? Explore our Services to see how Engine Analytics can support your data journey.
What Is Real-Time Data Processing?
Real-time data processing refers to capturing and analyzing data as soon as it is created. Instead of waiting, businesses act on insights instantly. This approach is critical in scenarios where every second counts.
Key Characteristics
Low latency: Data is processed in milliseconds or seconds.
Continuous flow: Information streams in and is immediately usable.
High responsiveness: Enables fast decision-making.
Common Use Cases
Fraud detection in banking.
Personalized product recommendations in e-commerce.
Live monitoring of IoT devices.
Real-time analytics for business dashboards.
By enabling fast responses, real-time data processing ensures that organizations don’t miss opportunities—or threats—that require immediate action.
What Is Batch Data Processing?
On the other side of the spectrum, batch data processing involves collecting and storing data until a specified period or volume is reached, and then processing it in bulk.
Key Characteristics
High throughput: Capable of handling large volumes of data.
Scheduled intervals: Often daily, weekly, or monthly.
Cost-efficient: Less demand on computing power in real time.

Batch Processing Use Cases
Payroll processing.
Monthly financial reporting.
Data archiving and backup.
Large-scale ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) operations.
For businesses that deal with structured, repetitive tasks, batch data processing provides a cost-effective and efficient solution.
Real-Time vs. Batch Data Processing: Core Differences
To fully understand Real-Time vs. Batch Data Processing, let’s compare the two approaches side by side.
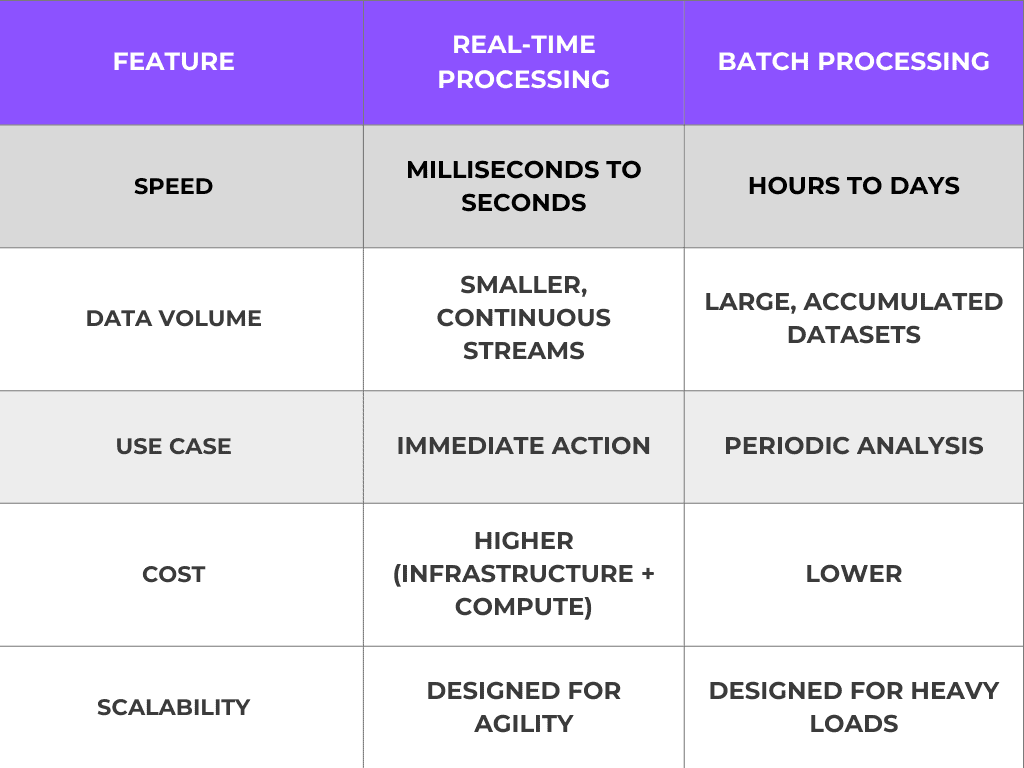
This comparison shows that neither approach is universally “better.” Instead, the right choice depends on your data processing strategies and business goals.
Benefits of Real-Time Data Processing
Faster decision-making – Ideal for industries like finance, where delays cost money.
Enhanced customer experience – Personalization in real time boosts loyalty.
Risk management – Detect anomalies, cyberattacks, or fraud as they happen.
Operational agility – Adjust strategies on the fly with real-time analytics for business.
? Want to dive deeper into building partnerships for analytics success? Check out our future post: What Makes a Great Data Analytics Partner?
Benefits of Batch Data Processing
Efficiency at scale – Handles terabytes of data without overwhelming systems.
Cost-effective – Less need for constant compute power.
Structured workflows – Ideal for repetitive, predictable tasks.
Historical insights – Enables long-term trend analysis for business intelligence.
Batch methods remain the backbone of many traditional systems, and they’re not going away anytime soon.
Which Data Processing Strategy Is Right for You?
When evaluating Real-Time vs. Batch Data Processing, ask yourself:
What are your business goals?
Need instant insights? Go real-time.
Need periodic reporting? Stick with batch.
What’s your data volume and velocity?
High-speed streams from IoT sensors ? Real-time.
Large archives of historical records ? Batch.
What’s your budget?
Real-time requires more infrastructure investment.
Batch can be more budget-friendly.
For many organizations, the answer isn’t one or the other—it’s a hybrid model that leverages both.

Hybrid Data Processing Strategies
Platforms like Apache Kafka are widely used to support real-time data processing, helping businesses handle streams of information with low latency.
Increasingly, businesses are blending both methods to get the best of both worlds:
Real-time analytics for business provides immediate visibility.
Batch processing use cases handle the heavy lifting of long-term data storage and compliance.
This hybrid strategy enables organizations to stay agile while also keeping costs under control.
? Curious about the tools that make hybrid strategies possible? Read our upcoming post: The Data Engineer’s Toolbox: Must-Have Tools for Seamless Analytics.
Real-World Examples
Cloud providers such as AWS also provide frameworks that blend both methods. The AWS Big Data Blog highlights best practices for designing systems that balance immediate insights with long-term storage.
Example 1: Retail Personalization
Retailers use real-time data processing to recommend products the moment customers browse online. Meanwhile, batch data processing helps them analyze seasonal buying trends.
Example 2: Healthcare Monitoring
Hospitals use real-time analytics for business to monitor patient vitals instantly, while batch processing use cases manage monthly reporting for compliance.
Example 3: Financial Services
Banks detect fraud in real time while relying on batch reports for quarterly audits.
These examples highlight why the Real-Time vs. Batch Data Processing conversation isn’t about “either/or”—it’s about balance.
Conclusion
When it comes to Real-Time vs. Batch Data Processing, there’s no universal answer. The right strategy depends on your goals, data needs, and resources. Real-time gives you speed and responsiveness; batch delivers scale and cost-efficiency.
By carefully aligning your data processing strategies with your business model, you can achieve both agility and efficiency.
Ready to explore the best solution for your organization? Visit our Services to learn more or get in touch via our Contact page. You can also start your journey with the Engine Analytics homepage for more insights.
Here’s Some Interesting FAQs for You
Q1: Is real-time data processing always better than batch processing?
Not necessarily. While real-time data processing is better for applications that demand instant insights—like fraud detection, customer personalization, or live system monitoring—it’s not always the most efficient or cost-effective approach. Batch data processing shines in scenarios where you’re dealing with massive amounts of structured data that don’t require immediate action, such as payroll, financial reporting, or data warehousing. The real decision isn’t about which method is “better” overall, but which method aligns best with your business goals, budget, and data volume. Many businesses find that the smartest approach is blending the two for optimal results.
Q2: Can businesses use both real-time and batch data processing?
Yes—and in fact, most successful organizations today rely on a hybrid model. For instance, an e-commerce business may use real-time analytics for business to deliver instant product recommendations, while running batch processing use cases like monthly revenue analysis or supply chain reporting in the background. This dual approach ensures companies can respond to immediate events while still leveraging deep, historical insights for long-term planning. Hybrid models also help balance costs, because not all workloads need the speed (and expense) of real-time systems.
Q3: Does real-time data processing cost more?
Typically, yes. Real-time data processing often requires advanced infrastructure such as streaming platforms (e.g., Apache Kafka), continuous data pipelines, and scalable cloud services. These systems consume more computing resources compared to scheduled batch jobs. However, the return on investment can be significant if fast insights prevent fraud, improve customer retention, or unlock competitive advantages. Batch data processing, by contrast, is less resource-intensive and often cheaper to run, but lacks the agility of real-time insights. The right choice depends on how much value immediate responsiveness brings to your business.
Not necessarily. While real-time data processing is better for applications that demand instant insights—like fraud detection, customer personalization, or live system monitoring—it’s not always the most efficient or cost-effective approach. Batch data processing shines in scenarios where you’re dealing with massive amounts of structured data that don’t require immediate action, such as payroll, financial reporting, or data warehousing. The real decision isn’t about which method is “better” overall, but which method aligns best with your business goals, budget, and data volume. Many businesses find that the smartest approach is blending the two for optimal results.
Yes—and in fact, most successful organizations today rely on a hybrid model. For instance, an e-commerce business may use real-time analytics for business to deliver instant product recommendations, while running batch processing use cases like monthly revenue analysis or supply chain reporting in the background. This dual approach ensures companies can respond to immediate events while still leveraging deep, historical insights for long-term planning. Hybrid models also help balance costs, because not all workloads need the speed (and expense) of real-time systems.
Typically, yes. Real-time data processing often requires advanced infrastructure such as streaming platforms (e.g., Apache Kafka), continuous data pipelines, and scalable cloud services. These systems consume more computing resources compared to scheduled batch jobs. However, the return on investment can be significant if fast insights prevent fraud, improve customer retention, or unlock competitive advantages. Batch data processing, by contrast, is less resource-intensive and often cheaper to run, but lacks the agility of real-time insights. The right choice depends on how much value immediate responsiveness brings to your business.








