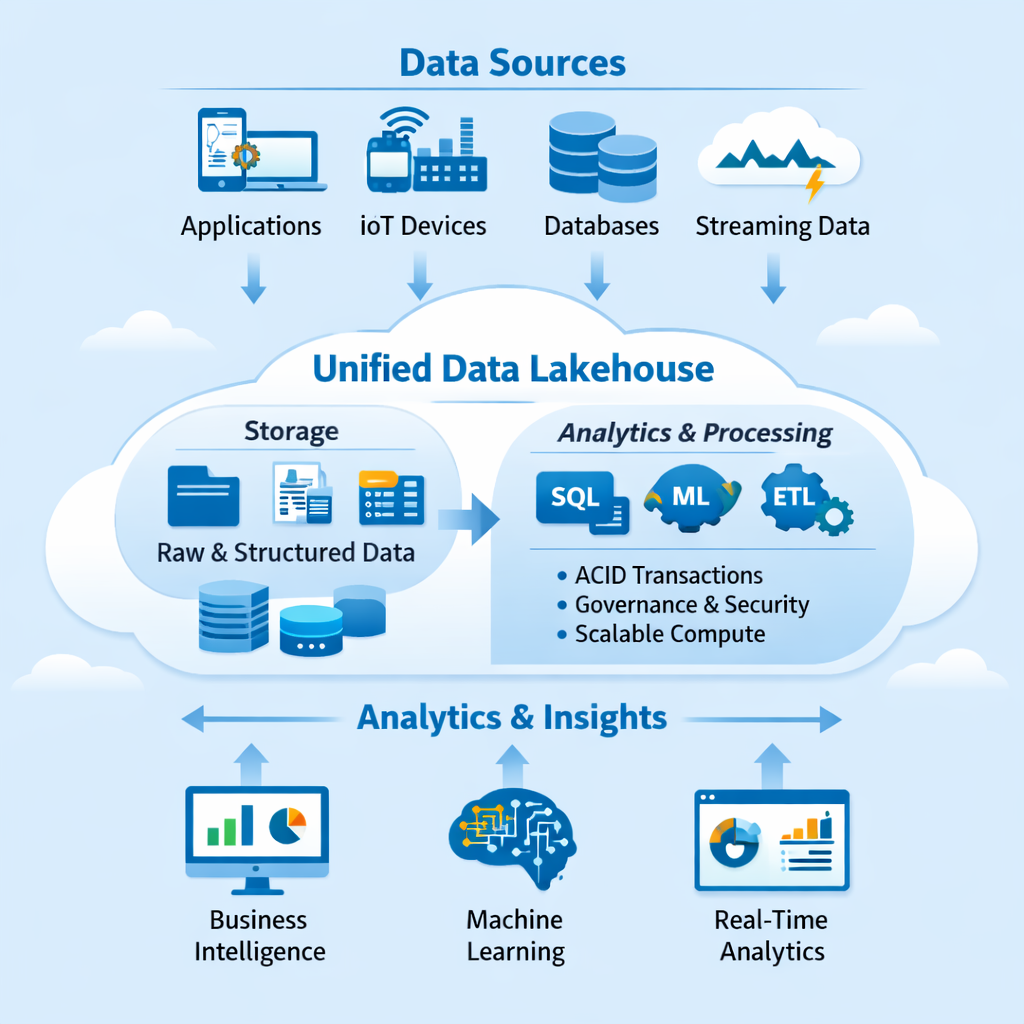
Core Components of a Modern Data Architecture
Unified Storage Layer
At the heart of a Modern Data Architecture is a unified storage layer. In lakehouse environments, this layer supports ACID transactions, schema evolution, and versioning. These features ensure reliability while keeping storage flexible and open.
Compute and Analytics Engines
Compute is decoupled from storage, allowing organizations to scale analytics workloads independently. This design supports everything from ad-hoc SQL queries to large-scale machine learning training.
By adopting Lakehouse Architectures, businesses gain a truly Unified Analytics Platform that serves multiple teams and use cases simultaneously.
Benefits of Lakehouse Architectures for Enterprises
Enhanced Data Accessibility
A lakehouse enables broader data access across departments. Analysts, data scientists, and engineers can work on the same datasets without creating isolated copies. This shared access fosters collaboration and accelerates insights.
Strong Governance and Security
Contrary to the misconception that data lakes lack control, Lakehouse Architectures introduce fine-grained governance. Features like role-based access control and auditing ensure compliance without slowing innovation.
Support for Advanced Analytics
From real-time dashboards to predictive models, lakehouses handle diverse workloads efficiently. This versatility is why many organizations now consider the Data Lakehouse model the foundation of their analytics strategy.
Optimizing Data Storage Through Scalability
Elastic Storage for Growing Data Volumes
Scalability is critical in today’s digital landscape. Scalable Data Storage allows organizations to handle sudden spikes in data without system redesigns. Lakehouses scale horizontally, ensuring consistent performance as data grows.
Performance Optimization Techniques
Lakehouse platforms use indexing, caching, and metadata management to boost query performance. These techniques ensure that Optimizing Data Storage does not come at the expense of speed or user experience.
Use Cases Where Lakehouse Architectures Excel
Business Intelligence and Reporting
Organizations can run interactive dashboards directly on lakehouse data, eliminating delays caused by ETL pipelines.
Machine Learning and AI
Data scientists benefit from direct access to raw and curated datasets, enabling faster experimentation and deployment.
Real-Time Analytics
Streaming data can be ingested and analyzed in near real time, supporting use cases like fraud detection and operational monitoring.
Best Practices for Implementing Lakehouse Architectures
Start with Clear Objectives
Before adoption, define business goals clearly. Whether the focus is Optimizing Data Storage, improving analytics, or reducing costs, alignment ensures success.
Invest in Governance Early
Strong governance frameworks prevent data chaos. Implement policies for access, quality, and lifecycle management from day one.
Partner with Experts
Working with experienced analytics providers can accelerate implementation. Organizations like Engine Analytics help design and deploy scalable lakehouse solutions tailored to business needs.